General Information/ IS derivatives of Tn3 family transposons
Another source of ambiguity for classification purposes occurs in the Tn3 family (see section “Tn families” and "Tn3 family") (Fig.10.1 and 10.2) [1]. Tn3 family members are quite variable. They include a number of diverse passenger genes that can represent entire operons, notably mercury resistance, or individual genes involved in antibiotic resistance, breakdown of halogenated aromatics, or virulence [e.g. [2]]. They often carry integron recombination platforms, enabling them to incorporate additional resistance genes by recruiting integron cassettes [3]. Members are quite characteristic: they have long relatively well conserved IR and a particularly long Tpase (950 to 1025 aa). They also encode a site-specific recombination (“resolution”) system necessary for completion of their transposition (Grindley 2002 - Chapter 14 from Mobile DNA II book). There are a number of different resolution systems associated with different members of this family (Fig.10.2) IS1071, (Fig.10.1) composed of Tn3-like IR and Tpase gene but lacking both the site-specific recombination system and passenger genes was identified many years ago[4][5]. This clearly accords with the definition of an IS. Several other examples have now been identified (e.g. ISVsa19, ISShfr9, ISBusp1).
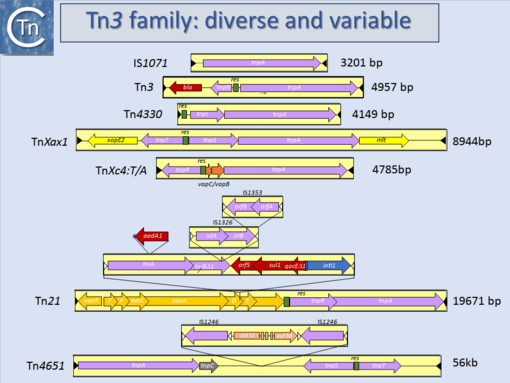 Fig.10.1. Tn3 family characteristics. Transposons are shown as yellow boxes with their names on the left and their lengths on the right. Terminal inverted repeats are shown as black arrowheads within the box. Transposition-related genes (transposases and resolvase recombinases are shown as purple arrows), passenger genes as red arrows, for antibiotic resistance orange/yellow arrows for heavy metal resistance, bright yellow for plant pathogenicity genes orange for toxin/antitoxin genes and blue for integron integrase genes. Resolution sites are shown in green. Note that Tn1071 carries only a transposase gene and therefore could be considered an Insertion sequence. |
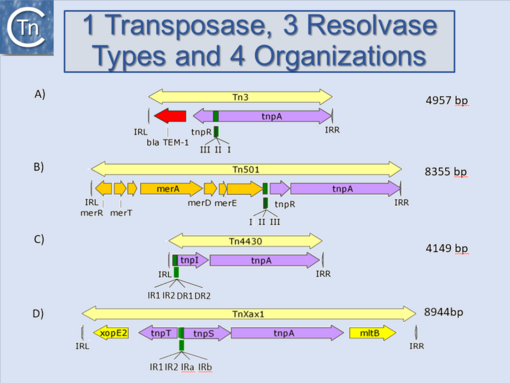 Fig.10.2. Tn3 family resolvase configuration. A) Tn3 has divergent transposase and resolvase (serine recombinase) genes with a res (resolution, recombination site between the divergent genes. It includes 3 sites at which resolvase binds (I, II and III). B) Tn501 carries co-linear transposase and resolvase genes with the res site upstream of the resolvase. C) Tn4430 has a similar configuration as Tn501 but its resolvase is a tyrosine recombinase and its res site, upstream of the resolvase has a more complex structure D) TnXax1 carries two divergent genes, tnpS (a serine recombinase) and tnpT (a helper gene). The resolution site lies between the two genes and has a complex structure (figure derived from [6]). |
Bibliography