Difference between revisions of "IS Families/IS481 family"
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Different members generate '''DR''' of between 4 and 15 bp. Moreover, certain members (e.g. [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=ISSav7 IS''Sav7'']) insert specifically into the tetranucleotide CTAG which becomes the flanking '''DR''' and provides the UAG termination codon for the Tpase. In contrast to the vast majority of [[IS Families/IS3 family|IS''3'' family]] members, the [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=IS481 IS''481''] Tpase is not produced by frameshifting. There is no evidence for a leucine zipper as in [[IS Families/IS3 family|IS''3''.]] | Different members generate '''DR''' of between 4 and 15 bp. Moreover, certain members (e.g. [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=ISSav7 IS''Sav7'']) insert specifically into the tetranucleotide CTAG which becomes the flanking '''DR''' and provides the UAG termination codon for the Tpase. In contrast to the vast majority of [[IS Families/IS3 family|IS''3'' family]] members, the [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=IS481 IS''481''] Tpase is not produced by frameshifting. There is no evidence for a leucine zipper as in [[IS Families/IS3 family|IS''3''.]] | ||
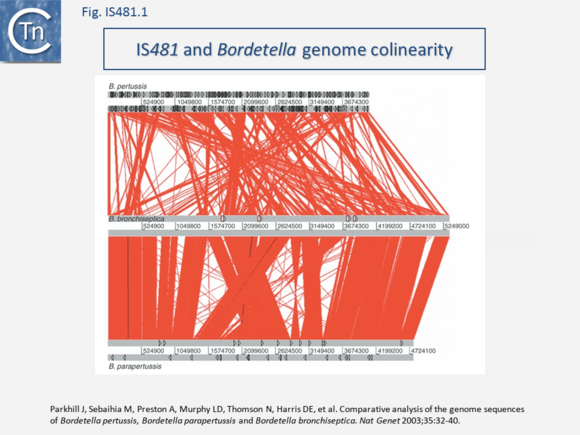
| − | Some members include passenger genes including antibiotic resistance ([[wikipedia:Chloramphenicol|Chloramphenicol]] - [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P94640 CmR] gene for [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=IS5564 IS''5564''] and [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=ISCgl1 IS''Cgl1'']), or potential transcriptional regulators ([https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=ISKrh1 IS''Krh1''], [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=ISPfr21 IS''Pfr21''], [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=ISSav7 IS''Sav7'']). [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=IS481 IS''481''] itself has played a fundamental role in the evolution of the genomes of the [[wikipedia:Bordetella|Bordetellae]] where, in ''[[wikipedia:Bordetella_pertussis|B. pertusis]]'' it has undergone extensive amplification to several hundred copies with accompanying genome decay<ref | + | Some members include passenger genes including antibiotic resistance ([[wikipedia:Chloramphenicol|Chloramphenicol]] - [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P94640 CmR] gene for [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=IS5564 IS''5564''] and [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=ISCgl1 IS''Cgl1'']), or potential transcriptional regulators ([https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=ISKrh1 IS''Krh1''], [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=ISPfr21 IS''Pfr21''], [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=ISSav7 IS''Sav7'']). [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=IS481 IS''481''] itself has played a fundamental role in the evolution of the genomes of the [[wikipedia:Bordetella|Bordetellae]] where, in ''[[wikipedia:Bordetella_pertussis|B. pertusis]]'' it has undergone extensive amplification to several hundred copies with accompanying genome decay<ref><pubmed>12910271</pubmed></ref><ref><pubmed>15100691</pubmed></ref> [[:File:Fig. IS481.png|(Fig.IS481.1)]], |
[[File:Fig. IS481.png|center|thumb|580x580px|'''Fig. IS481.1.''' Colinearity between the genomes of ''[[wikipedia:Bordetella_pertussis|B. pertussis]]'' ('''Top''')'','' ''[[wikipedia:Bordetella_bronchiseptica|B. bronchiseptica]]'' ('''Center''') and ''[[wikipedia:Bordetella_parapertussis|B. parapertussis]]'' (''Bottom'')'''. Top''': ''B. pertussis''. Black triangles represent IS''481'' elements. '''Center:''' ''B. bronchiseptica''. Pink boxes represent prophage. '''Bottom:''' ''B. parapertussis''. Black triangles represent [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=IS481 IS''481''] elements. The red lines between the genomes represent BLASTN matches between the two sequences. (extracted from: [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12910271/ Parkhill J, Sebaihia M, Preston A, Murphy LD, Thomson N, Harris DE, et al. Comparative analysis of the genome sequences of ''Bordetella pertussis'', ''Bordetella parapertussis'' and ''Bordetella bronchiseptica. Nat Genet'' 2003;35:32-40].)]] | [[File:Fig. IS481.png|center|thumb|580x580px|'''Fig. IS481.1.''' Colinearity between the genomes of ''[[wikipedia:Bordetella_pertussis|B. pertussis]]'' ('''Top''')'','' ''[[wikipedia:Bordetella_bronchiseptica|B. bronchiseptica]]'' ('''Center''') and ''[[wikipedia:Bordetella_parapertussis|B. parapertussis]]'' (''Bottom'')'''. Top''': ''B. pertussis''. Black triangles represent IS''481'' elements. '''Center:''' ''B. bronchiseptica''. Pink boxes represent prophage. '''Bottom:''' ''B. parapertussis''. Black triangles represent [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=IS481 IS''481''] elements. The red lines between the genomes represent BLASTN matches between the two sequences. (extracted from: [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12910271/ Parkhill J, Sebaihia M, Preston A, Murphy LD, Thomson N, Harris DE, et al. Comparative analysis of the genome sequences of ''Bordetella pertussis'', ''Bordetella parapertussis'' and ''Bordetella bronchiseptica. Nat Genet'' 2003;35:32-40].)]] | ||
| − | These IS are distantly related to the eukaryotic Banshee transposon which at present is restricted to the anaerobic flagellated protozoan ''[[wikipedia:Trichomonas_vaginalis|Trichomonas vaginalis]]'' ([https://www.bioscience.utah.edu/faculty/pritham/ Pritham] per. comm.)<ref | + | These IS are distantly related to the eukaryotic Banshee transposon which at present is restricted to the anaerobic flagellated protozoan ''[[wikipedia:Trichomonas_vaginalis|Trichomonas vaginalis]]'' ([https://www.bioscience.utah.edu/faculty/pritham/ Pritham] per. comm.)<ref><pubmed>18076328</pubmed></ref>. They share the highly conserved [https://pfam.xfam.org/family/PF00552 Pfam integrase core domain] identified initially in the [[IS Families/IS3 family|IS''3'' family]] and [[wikipedia:Retrovirus|retroviruses]]<ref><pubmed>1963920</pubmed></ref><ref><pubmed>1314954</pubmed></ref>. They also show a conserved '''5’''' TG '''3’''' tip to the '''IR''' which is typical of this and other types of mobile elements. It would be interesting to determine whether Banshee transposes using a dsDNA circular intermediate as do [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/TnPedia/index.php/IS_Families/IS3_family IS''3'' family members]. |
=====IS''1202'' group (IS''NCY'')===== | =====IS''1202'' group (IS''NCY'')===== | ||
| − | A small group including [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=IS1202 IS''1202'']<ref | + | A small group including [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=IS1202 IS''1202'']<ref><pubmed>8021229</pubmed></ref>, which had been included in the IS''NCY'' ('''N'''ot '''C'''lassified '''Y'''et) group appears distantly related to IS''481''. Members are between 1400 and 1700 bp (except for [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=ISKpn21 IS''Kpn21''] which includes a passenger gene annotated as "[[wikipedia:Hypothetical_protein|hypothetical protein]]”) with a Tpase orf of between 400 and 500 aa in a single reading frame. Their IR begin with TGT as do those of the [[IS Families/IS3 family|IS''3'']] and IS''481'' families. They generate '''DR''' of between 5 and, unusually, 27 bp. |
They appear to have similarities at the level of their Tpases particularly in their DDE domains (e.g. [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=IS1202 IS''1202''] is 39% aa similar to [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=ISPfr5 IS''Pfr5''] of the IS''481'' family). Furthermore, they include glutamine ('''Q''') seven residues C-terminal to the conserved '''E''' instead of the characteristic '''K/R'''. Identification of additional IS will be necessary to clearly define this group. <br /> | They appear to have similarities at the level of their Tpases particularly in their DDE domains (e.g. [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=IS1202 IS''1202''] is 39% aa similar to [https://tncentral.ncc.unesp.br/ISfinder/scripts/ficheIS.php?name=ISPfr5 IS''Pfr5''] of the IS''481'' family). Furthermore, they include glutamine ('''Q''') seven residues C-terminal to the conserved '''E''' instead of the characteristic '''K/R'''. Identification of additional IS will be necessary to clearly define this group. <br /> | ||
==Bibliography== | ==Bibliography== | ||
| − | < | + | {{Reflist|32em}} |
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | {{TnPedia}} | ||
Latest revision as of 12:52, 5 December 2022
General
Initially, IS481 appeared to be an IS3 family derivative which had been truncated for the N-terminal end of the Tpase and includes a C-terminal extension. The DDE active site domain and the IR (ending in 5’ TGT 3’) are similar to those of IS3 family members. Their presence in high copy number in some species and the identification of at least 130 distinct but related IS from over 90 species strongly suggests that these represent a distinct transpositionally active family.
Different members generate DR of between 4 and 15 bp. Moreover, certain members (e.g. ISSav7) insert specifically into the tetranucleotide CTAG which becomes the flanking DR and provides the UAG termination codon for the Tpase. In contrast to the vast majority of IS3 family members, the IS481 Tpase is not produced by frameshifting. There is no evidence for a leucine zipper as in IS3.
Some members include passenger genes including antibiotic resistance (Chloramphenicol - CmR gene for IS5564 and ISCgl1), or potential transcriptional regulators (ISKrh1, ISPfr21, ISSav7). IS481 itself has played a fundamental role in the evolution of the genomes of the Bordetellae where, in B. pertusis it has undergone extensive amplification to several hundred copies with accompanying genome decay[1][2] (Fig.IS481.1),
These IS are distantly related to the eukaryotic Banshee transposon which at present is restricted to the anaerobic flagellated protozoan Trichomonas vaginalis (Pritham per. comm.)[3]. They share the highly conserved Pfam integrase core domain identified initially in the IS3 family and retroviruses[4][5]. They also show a conserved 5’ TG 3’ tip to the IR which is typical of this and other types of mobile elements. It would be interesting to determine whether Banshee transposes using a dsDNA circular intermediate as do IS3 family members.
IS1202 group (ISNCY)
A small group including IS1202[6], which had been included in the ISNCY (Not Classified Yet) group appears distantly related to IS481. Members are between 1400 and 1700 bp (except for ISKpn21 which includes a passenger gene annotated as "hypothetical protein”) with a Tpase orf of between 400 and 500 aa in a single reading frame. Their IR begin with TGT as do those of the IS3 and IS481 families. They generate DR of between 5 and, unusually, 27 bp.
They appear to have similarities at the level of their Tpases particularly in their DDE domains (e.g. IS1202 is 39% aa similar to ISPfr5 of the IS481 family). Furthermore, they include glutamine (Q) seven residues C-terminal to the conserved E instead of the characteristic K/R. Identification of additional IS will be necessary to clearly define this group.
Bibliography
- ↑ Parkhill J, Sebaihia M, Preston A, Murphy LD, Thomson N, Harris DE, Holden MT, Churcher CM, Bentley SD, Mungall KL, Cerdeño-Tárraga AM, Temple L, James K, Harris B, Quail MA, Achtman M, Atkin R, Baker S, Basham D, Bason N, Cherevach I, Chillingworth T, Collins M, Cronin A, Davis P, Doggett J, Feltwell T, Goble A, Hamlin N, Hauser H, Holroyd S, Jagels K, Leather S, Moule S, Norberczak H, O'Neil S, Ormond D, Price C, Rabbinowitsch E, Rutter S, Sanders M, Saunders D, Seeger K, Sharp S, Simmonds M, Skelton J, Squares R, Squares S, Stevens K, Unwin L, Whitehead S, Barrell BG, Maskell DJ . Comparative analysis of the genome sequences of Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica. - Nat Genet: 2003 Sep, 35(1);32-40 [PubMed:12910271] [DOI]
- ↑ Preston A, Parkhill J, Maskell DJ . The bordetellae: lessons from genomics. - Nat Rev Microbiol: 2004 May, 2(5);379-90 [PubMed:15100691] [DOI]
- ↑ Feschotte C, Pritham EJ . DNA transposons and the evolution of eukaryotic genomes. - Annu Rev Genet: 2007, 41;331-68 [PubMed:18076328] [DOI]
- ↑ Fayet O, Ramond P, Polard P, Prère MF, Chandler M . Functional similarities between retroviruses and the IS3 family of bacterial insertion sequences? - Mol Microbiol: 1990 Oct, 4(10);1771-7 [PubMed:1963920] [DOI]
- ↑ Kulkosky J, Jones KS, Katz RA, Mack JP, Skalka AM . Residues critical for retroviral integrative recombination in a region that is highly conserved among retroviral/retrotransposon integrases and bacterial insertion sequence transposases. - Mol Cell Biol: 1992 May, 12(5);2331-8 [PubMed:1314954] [DOI]
- ↑ Morona JK, Guidolin A, Morona R, Hansman D, Paton JC . Isolation, characterization, and nucleotide sequence of IS1202, an insertion sequence of Streptococcus pneumoniae. - J Bacteriol: 1994 Jul, 176(14);4437-43 [PubMed:8021229] [DOI]